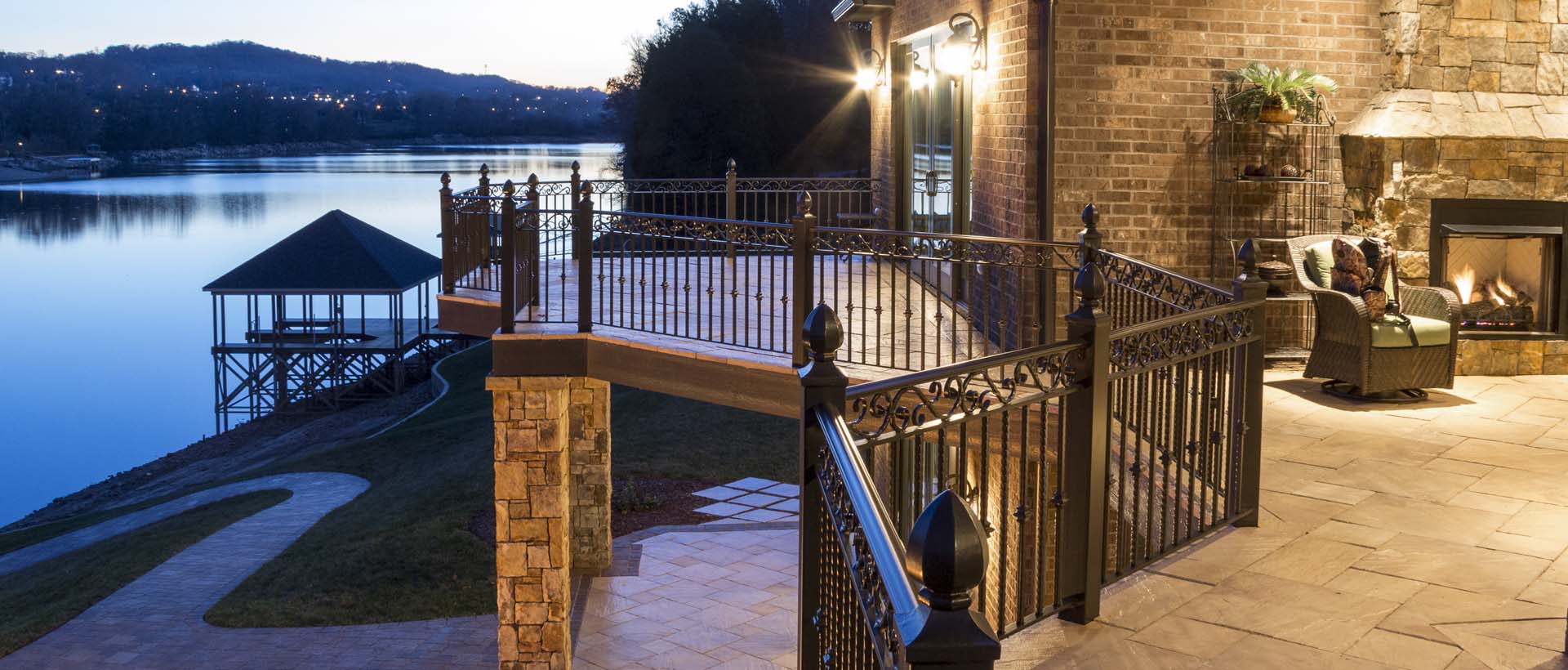
Pedestal Decking
Why Pedestal Decking?
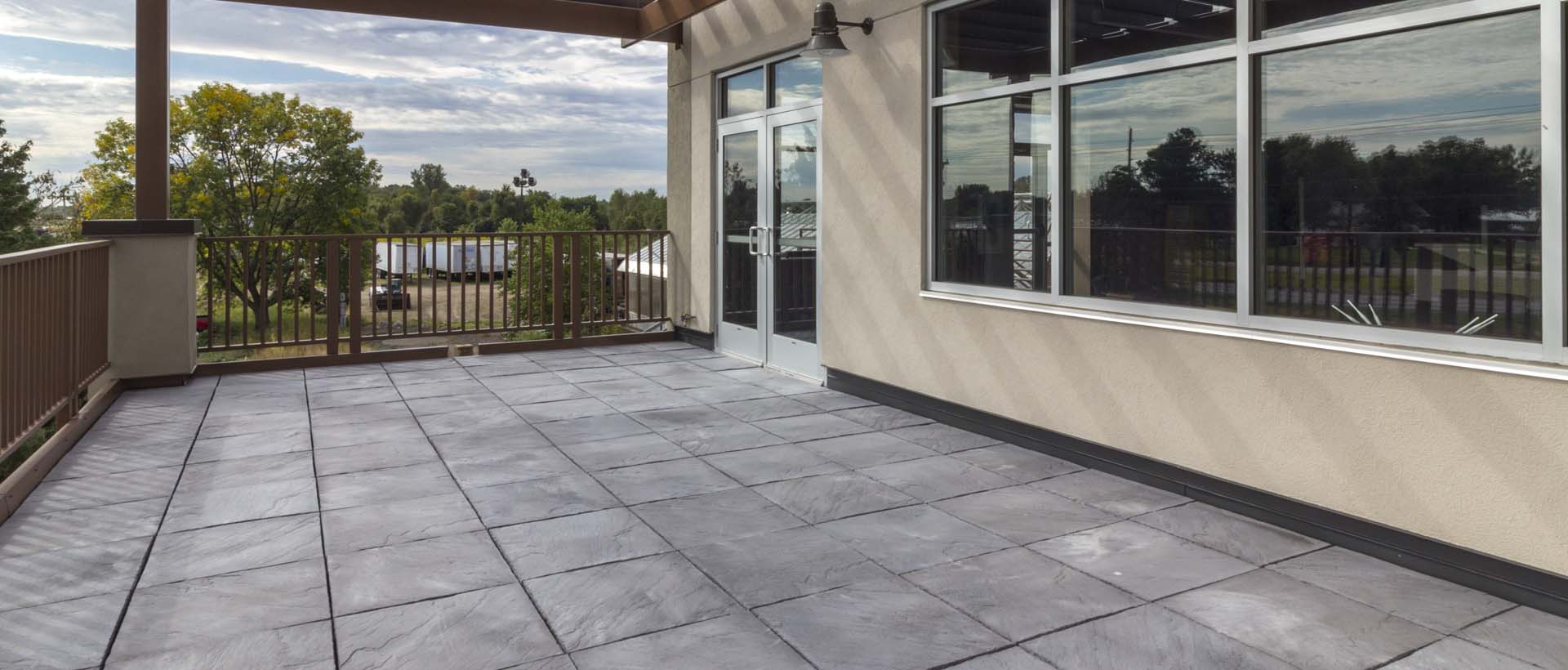
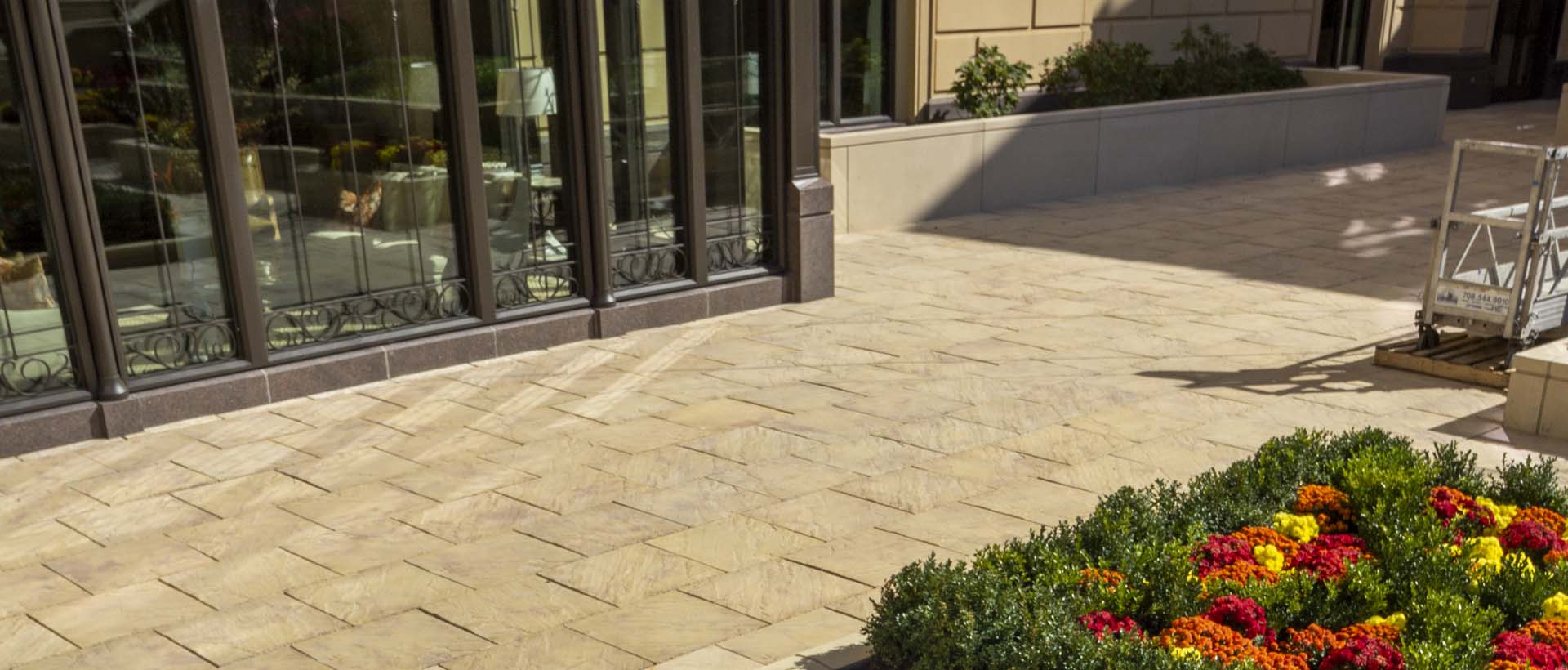
- Provide an attractive, durable surface for pedestrian plaza and roof decks.
- Create valuable outdoor spaces, usable exterior living environments.
- Protect roofing materials from foot traffic, equipment, and elements.
- Acts as a heat sink to reduce thermal stress and deterioration of waterproofing materials.
- Exhibit high durability under freeze-thaw and deicing/salt exposure.
- Provide a consistent, evenly distributed weight for protection from wind uplift and damage.
- Vegetated, low-slope roof surfaces or “green roofs” reduce building energy costs and urban heat effect.
The Components
Geotextiles
- With sand or aggregate bedding materials, geotextile will be needed to contain them and keep them from migrating into deck drains.
Protection board
- Most waterproofing systems require a protection board over them to prevent damage to the waterproofing from paving units and to reduce thermal stresses from temperature changes.
Insulation
- If a pedestrian plaza deck covers an inhabited space, insulation may be required. Insulation typically consists of foam or fiber boards placed over the waterproofing.
Drainage mats
- Drainage mats are generally placed under bedding sand and over waterproof membranes to accelerate drainage of water from the sand. Drainage mats are typically ¼” to ⅜” thick.
Design Considerations
Detailing
- Detailing of roof joints, edge restraints, and expansion materials. As well as detailing for vehicular applications.
Weight
- The advice of a structural engineer should be sought to assess the capacity of the roof and tolerable deflections from paving-related loads.
Resistance to Wind Uplift
- Some high wind regions may have local building codes with additional weight requirements for paving units, especially on high-rise buildings.
Slope for Drainage
- Use deck systems that enable construction of a minimum 2% slope as some toppings are not waterproof and flat roofs will eventually leak.
Slopes for Pedestrians and Vehicles
- Maximum percentage is typically 8% for pedestrians, 20% for vehicles.
Roof Drains
Raising Elevations
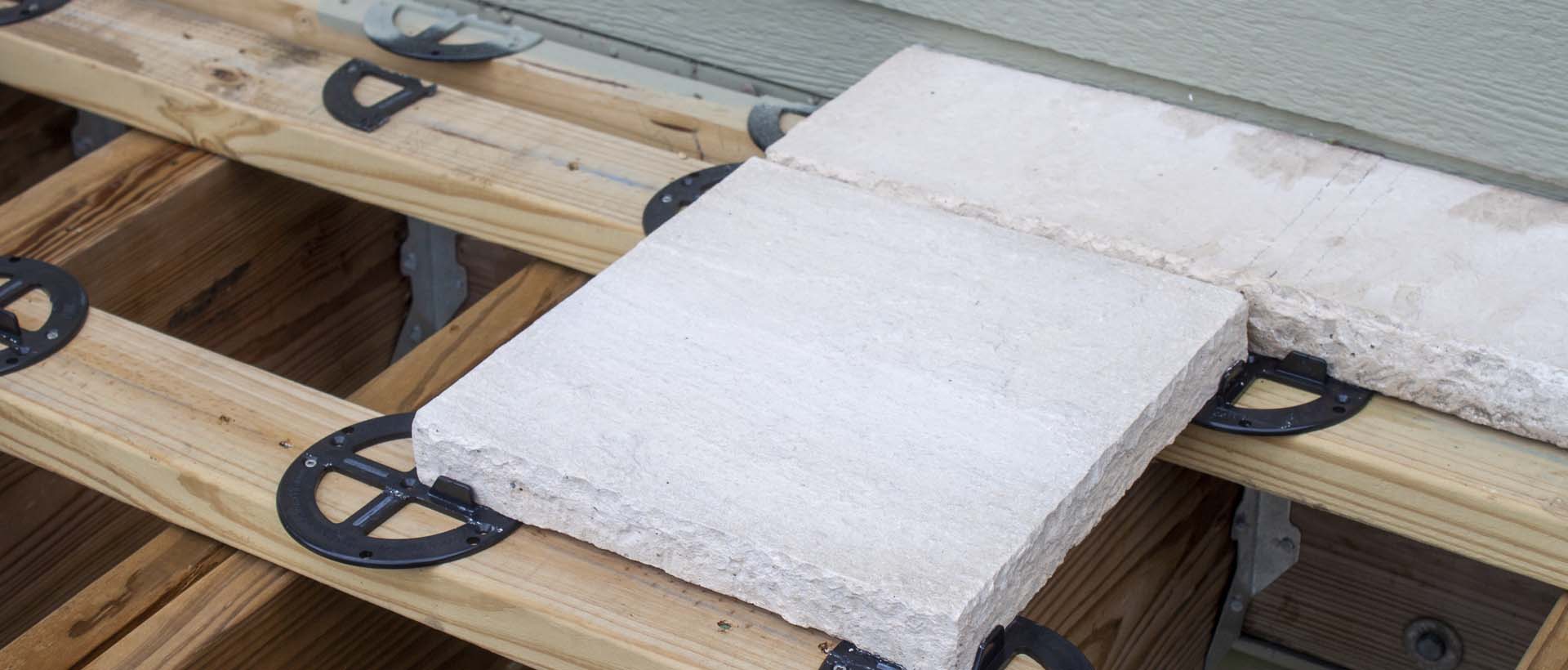
Deck Joist System
A Joist Plate System is a sister interlocking system, using joist plate component and top shim components. This allows easy installation of concrete pavers, natural gauged stone, and other architectural slabs over wood joists. This system easily adapts to new and old decks, virtually ending the drudgery of maintaining a wood slat deck.
4x6's should be used in new construction, or sistering 2x4's with 2x4's should provide a working under-layment. If deck is suspended, engineering may be required to support the weight. Consult a specialist regarding load and structural requirements.
LEED Credits Available
SS credit 7.1 (Heat Island Effect: Non-Roof)
- Shade constructed surfaces on site with landscape features and utilize high-reflectance hardscape materials. Consider replacing constructed surfaces (i.e. roof, roads, sidewalks, etc.) with vegetated surfaces such as vegetated roofs and open grid paving or specify high-albedo materials to reduce heat absorption.
- Paving materials with a Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) of at least 29
SS Credit 5.2 (Maximize Open Space)
- Provide a high ratio of open space to development footprint to promote biodiversity. For projects located in urban areas that earn SS Credit 2, pedestrian oriented hardscape areas can contribute to credit compliance. For such projects, a minimum of 25% of the open space counted must be vegetated.
SS Credit 6.1 (Storm water Design: Quantity Control)
- Design the project site to maintain natural storm water flows by promoting infiltration. Specify vegetated roofs, pervious paving, and other measures to minimize impervious surfaces. Reuse storm water volumes generated for non-potable uses such as landscape irrigation, toilet flushing and custodial uses.
SS Credit 6.2 (Storm water Design: Quality Control)
- Use alternative surfaces (e.g., vegetated roofs, pervious pavement or grid pavers) and non structural techniques(e.g., rain gardens, vegetated swales, disconnection of imperviousness, rainwater recycling) to reduce imperviousness and promote infiltration thereby reducing pollutant loadings.
MR Credit 5.1 (Regional Materials: 10% and MR Credit 5.2 Regional Materials: 20%)
- Use building materials or products that have been extracted, harvested or recovered, as well as manufactured, within 500 miles of the project site for a minimum of 10% (based on cost) of the total materials value. If only a fraction of a product or material is extracted/harvested/recovered and manufactured locally, then only that percentage (by weight) shall contribute to the regional value. Mechanical, electrical and plumbing components and specialty items such as elevators and equipment shall not be included in this calculation.
- Only include materials permanently installed in the project. Furniture may be included, providing it is included consistently in MR Credits 3–7.
ID Credit 1-1.4 (Innovation in Design)
- To provide design teams and projects the opportunity to be awarded points for exceptional performance above the requirements set by the LEED for New Construction Green Building Rating System and/or innovative performance in Green Building categories not specifically addressed by the LEED for New Construction Green Building Rating System.